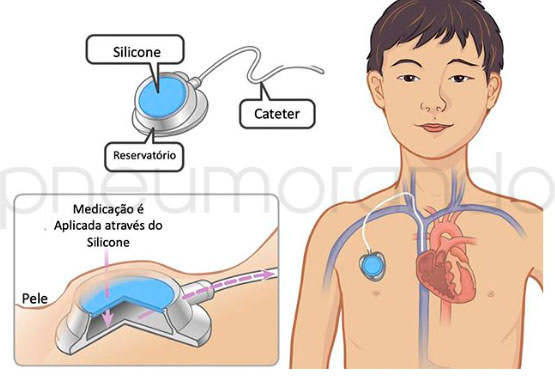



O dispositivo de port-a-cath, é totalmente implantado sob a pele, e permite fácil acesso às veias do paciente. A ponta do cateter deve ficar posicionada em uma veia de grande calibre (geralmente veia cava superior) e a extremidade distal é acoplada ao reservatório. A extremidade distal é acoplada ao reservatório, que permanece no tecido subcutâneo no tórax, usualmente logo abaixo da clavícula.
Ele se divide em duas partes: o cateter, feito de silicone ou poliuretano, e o reservatório, constituído de titânio e/ou plástico resistente coberto por um septo de silicone puncionável. O silicone especial autovendante, pode ser perfurado por uma agulha várias vezes antes que a resistência do material seja comprometida. Seu design contribui para um risco muito baixo de infecção.